
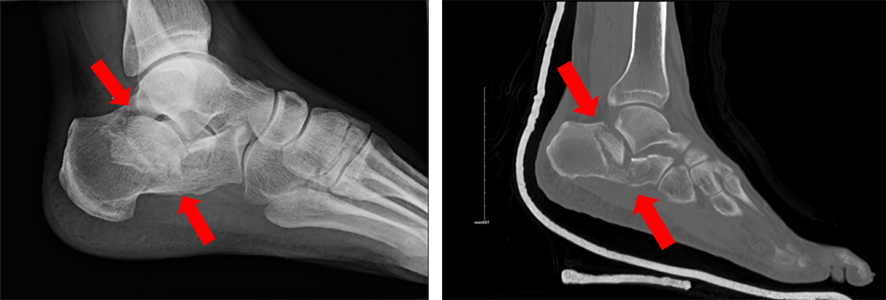
Methods: Patients with intra-articular calcaneus fractures managed operatively over 10 years with a minimum six-month follow-up were included. We retrospectively analyzed patient outcomes of a single surgeon’s experience in treating these injuries at a busy urban Level 1 trauma center. These injuries pose a challenge to patients as they often result in poor patient outcomes. Open techniques have been associated with an increased risk of wound complications, while percutaneous techniques may result in inferior reduction capabilities. * Corresponding author: Percutaneous reduction with fixation and open reduction internal fixation are often used to treat intra-articular calcaneus fractures with no consensus on the preferred method. After complete recovery, the patient can resume their daily living with normal activities.Kevin Steelman *, Nicholas Bolz, Enrique Feria-Arias and Robert Meehanĭetroit Medical Center, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Harper University Hospital, 3990 John R, Detroit, MI 48201, USA Metal screws are then inserted and fixed through small incisions to hold the bone pieces together.įollowing treatment, the patient is recommended to perform simple exercises and undergo physical therapy to help restore flexibility and function. The bone can either be pushed or pulled to set into place without making a large incision. Percutaneous screw fixation – This is the best preferred treatment when the broken bone pieces are large.

Open reduction and internal fixation – This surgery involves putting the bone fragments back together with metal plates and screws to reposition them and set them to normal alignment.Walking with the help of crutches is advised to avoid bearing your body weight until healing has occurred. Immobilization – Casting the injured foot prevents the fractured bone from moving.Positioning the foot above the level of your heart helps reduce swelling. Compression stockings and elastic bandages can also aid in alleviating pain. Covering the affected area with ice packs over a towel reduces swelling and pain. Staying off (resting) the injured foot can alleviate the symptoms to a great extent. Rest, ice, compression and elevation (R.I.C.E.) is the most commonly used treatment option.Inability to walk or bear weight on the injured footĬalcaneus fractures are diagnosed with an X-ray or CT scan.Ĭalcaneal fractures are treated based on the type of fracture and extent of soft tissue damage.The common signs and symptoms of calcaneal fractures are Stiffness and pain in the joint, and arthritis are common risks following a calcaneal fracture. A calcaneus fracture can be categorized as a stable fracture, displaced fracture, open fracture, closed fracture or comminuted fracture, depending on its severity.Ī fracture of the calcaneus occurs most commonly due to a traumatic event such as falling from a height, twisting injury, motor accident, sports injury or ankle sprain.Ī fracture of the calcaneus is considered serious and can cause longstanding problems if not treated effectively. A fracture is a break in a bone following trauma or due to various conditions. The calcaneus connects with the talus and cuboid bones to form the subtalar joint of the foot. The calcaneus or heel bone is a large bone found at the rear end of the foot. Home » Patient Resources » General Orthopaedics » Fractures/Dislocations » Heel Fractures Heel Fractures


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
